SAEDNEWS; Why Your Muscles Keep Cramping or Cause Persistent Pain and Burning Sensations
According to SaedNews Health Service, muscles in the body aren’t always in perfect condition. At times, for a variety of scientific reasons, they can experience tightness, pain, or a burning sensation, which concerns many people. The causes, however, can be surprisingly interesting. Here’s what you need to know.
Muscles don’t always feel the same throughout life. Sometimes they cause discomfort or pain. When muscles aren’t functioning properly, injuries or aches can occur. But where does this pain actually come from?
If you feel burning or discomfort in your feet, the culprit might be a small muscle at the base of your big toe called the flexor hallucis longus. Weakness in the hips can put extra stress on other areas, including the feet. This muscle helps maintain balance while walking and prevents falls.
Prevention tips: Strengthen your leg and hip muscles through exercises like squats and lunges. Wearing supportive shoes and occasionally walking barefoot can also help strengthen the muscles in your feet.
Some back pain stems from a weak lower back and a small muscle called the piriformis, which covers the hip and helps rotate the pelvis.
Prevention tips: Engage your knees while walking, and try exercises using a stability ball—sitting on the ball and performing rotational movements strengthens this muscle.
Neck pain often involves the scalene muscles, which run along the sides of the neck.
Prevention tips: Strengthen your upper back and shoulders, and maintain proper neck posture to avoid strain.
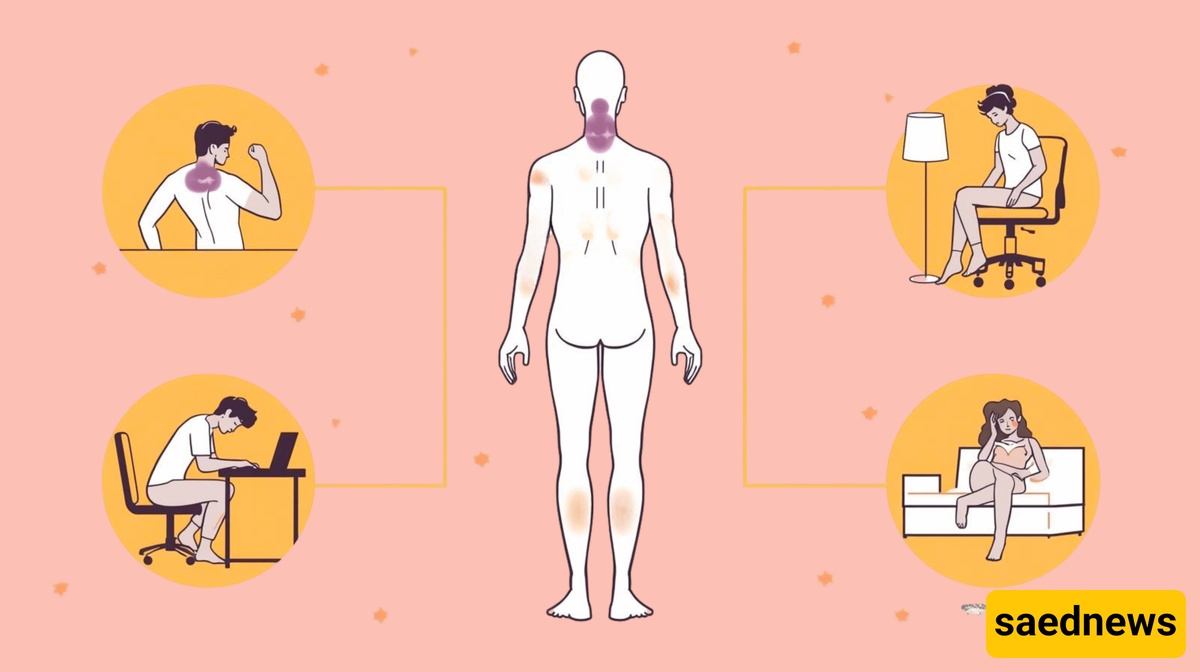
Two key muscle groups linked to lower back pain are the multifidus and the psoas. The psoas, located inside the pelvis, becomes tight when you sit for long periods. The multifidus, a thin muscle connected to the vertebrae, stabilizes and supports the spine. Studies show that training these muscles can significantly reduce lower back pain.
Prevention tips: Avoid prolonged sitting. Stand up and walk for at least two minutes every hour, especially if you spend a lot of time seated.
Shoulder pain often coincides with neck discomfort. It may originate from a small muscle called the levator scapulae, located at the top of the back and connected to the shoulder blade. Forward-leaning posture can trigger pain in this area.
Prevention tips: Keep your back straight to reduce pressure, and perform light-weight exercises—raising weights along your sides while slightly bending forward—to strengthen the shoulder blades. Focus on engaging both shoulder blades simultaneously.
Prevention is key. On the first or second day of pain, use a cold compress. If swelling occurs, wrap the area, and only use anti-inflammatory medication like ibuprofen under a doctor’s supervision. Rest the affected muscle for a few days. Pain may temporarily worsen before improvement, but if severe pain persists after 3–4 days, it may indicate a serious injury requiring medical attention.

