SAEDNEWS: Symptoms of miscarriage or pregnancy termination include vaginal bleeding, cramping or abdominal pain, passing tissue or blood clots from the uterus, and a decrease in pregnancy symptoms. However, sometimes it may be accompanied by different symptoms. For more information on this topic, follow the rest of the article on Saed News.

According to SAEDNEWS, Symptoms of miscarriage during pregnancy may include vaginal bleeding, abdominal pain, severe muscle contractions, and the loss of fetal movement signs. The World Health Organization (WHO) identifies miscarriage as one of the most significant pregnancy risks, characterized by heavy discharge or bleeding in the first half of pregnancy without cervical dilation.
Approximately 25% of pregnant women experience vaginal bleeding during the first two to three months of pregnancy, and about 50% of these cases result in miscarriage. If you experience intermittent muscle cramps, pain in the pubic area, pelvic pressure, or lower back pain without a known cause, do not hesitate to consult a gynecologist or obstetrician. Stay with us until the end of this article as we explore the most important signs of miscarriage during pregnancy.
Miscarriage usually presents with certain signs, though symptoms can vary from person to person. Some of the most common include:
For most women, this is the first sign of miscarriage. Bleeding can range from light spotting to heavy bleeding, similar to a menstrual period.
Uterine contractions and abdominal pain, similar to menstrual cramps, can occur during a miscarriage and may range from mild to severe.
You may notice tissue or blood clots passing from the vagina, varying in size and sometimes accompanied by heavy bleeding.
If symptoms like breast tenderness, nausea, or fatigue suddenly disappear, it may be a reason for concern.
Some women experience back pain during a miscarriage.
However, not all cases of vaginal bleeding or abdominal pain indicate a miscarriage. If you experience any of these symptoms, consult a gynecologist or obstetrician for an accurate diagnosis and guidance.

The first sign of a potential miscarriage is often vaginal bleeding accompanied by muscle cramps. However, not all cases of bleeding and abdominal pain during pregnancy indicate miscarriage.
Pregnancy-related bleeding may sometimes appear as light spotting, often mistaken for a menstrual period. In other cases, bleeding may be heavier (accompanied by clots) and come with abdominal pain and cramping.
While abdominal pain can be a symptom of miscarriage, not all abdominal pain during pregnancy is linked to miscarriage. Cramping and pain during this period can be severe (similar to post-exercise soreness) and may be accompanied by bleeding.
However, muscle contractions may also be due to other factors, such as:
Natural hormonal changes
Gas and bloating
Digestive issues
Round ligament pain
During pregnancy and after miscarriage, temporary weight changes may occur due to hormonal fluctuations, emotional stress, or changes in appetite. It's essential to remain calm and seek medical advice.
A sudden disappearance of pregnancy symptoms can be concerning. However, pregnancy symptoms vary among individuals. Some women experience nausea, hot flashes, and drastic weight changes throughout pregnancy, while others only have these symptoms briefly.
Possible reasons for disappearing pregnancy symptoms:
Hormonal changes: As hormone levels adjust, symptoms may come and go.
Different pregnancy stages: Symptoms are usually more pronounced in the first trimester and may fade in the second trimester.
Fatigue and stress: Physical and emotional stress can impact the body’s functions.
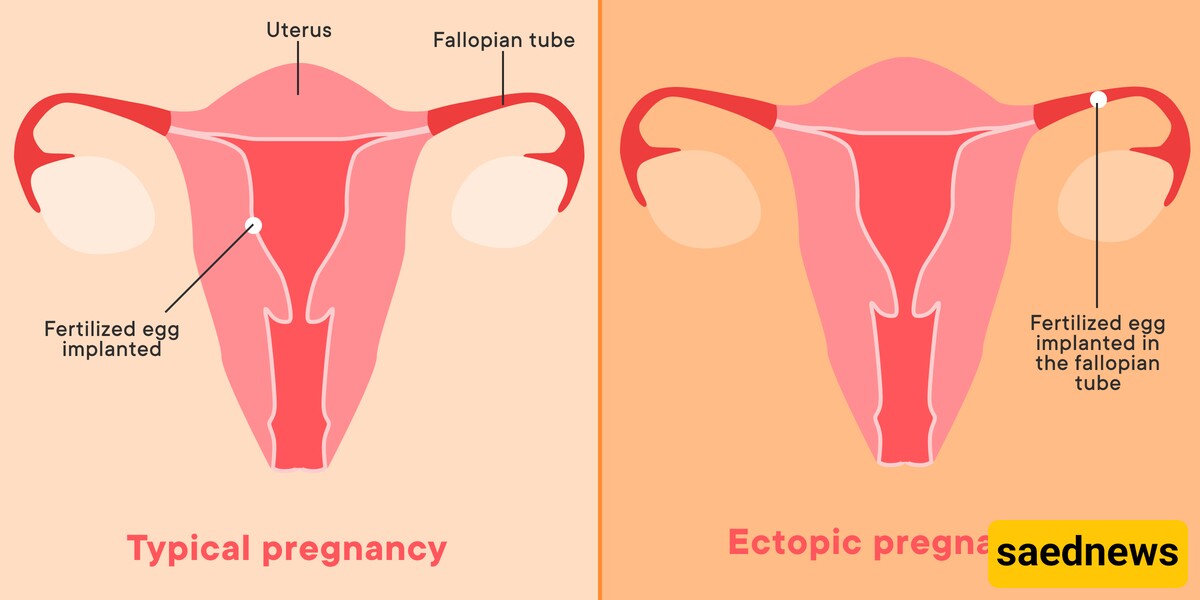
Uterine rupture is a rare but serious complication that can occur during pregnancy or labor. It is typically associated with prior uterine surgeries, such as cesarean sections or myomectomy (fibroid removal surgery). Although uterine rupture is not directly linked to miscarriage, it should be managed under medical supervision.
Fetal movement is an important indicator of pregnancy health. A sudden decrease or lack of movement can be concerning.
Fetal movement varies throughout the day and may decrease due to:
Baby’s position in the womb
Mother's activity level
Baby’s sleep cycle
If you notice a significant reduction in fetal movement, seek medical evaluation. Your doctor may use kick counts, ultrasound, or other tests to assess fetal well-being.
While bleeding is a common symptom, some women experience miscarriage without it. Other symptoms may include:
Pelvic pressure: A feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen.
Changes in vaginal discharge: Increased discharge, especially if watery, pink, or containing tissue.
Passing large tissue or blood clots (without bleeding): Some miscarriages occur without noticeable tissue expulsion.
Navel pain is not typically a direct symptom of miscarriage. However, some women may experience discomfort or pain in the navel and abdomen during a miscarriage.
Spotting during pregnancy can be a sign of miscarriage and usually appears as light pink or brown bleeding. However, not all cases of spotting lead to miscarriage.
Trimester | Possible Symptoms |
|---|---|
First Trimester (Weeks 1-13) | - Vaginal bleeding (light to heavy) |
Abdominal cramps similar to menstrual pain |
| Second Trimester (Weeks 14-27) | - Vaginal bleeding and uterine contractions
Passing tissue or clots
Lower back or lower abdominal pain |
| Third Trimester (Week 28 and beyond) | - Severe and persistent abdominal pain
Sudden loss of pregnancy symptoms
No fetal movement |
All symptoms mentioned in this article serve as warning signs of miscarriage and indicate when to seek medical attention. To support a healthy pregnancy, consider:
Avoiding alcohol, smoking, or recreational drug use
Avoiding exposure to harmful chemicals and toxins
Taking prenatal vitamins with folic acid
Maintaining a healthy diet rich in fruits and vegetables
Exercising for 20-30 minutes daily
Managing infections and underlying health conditions
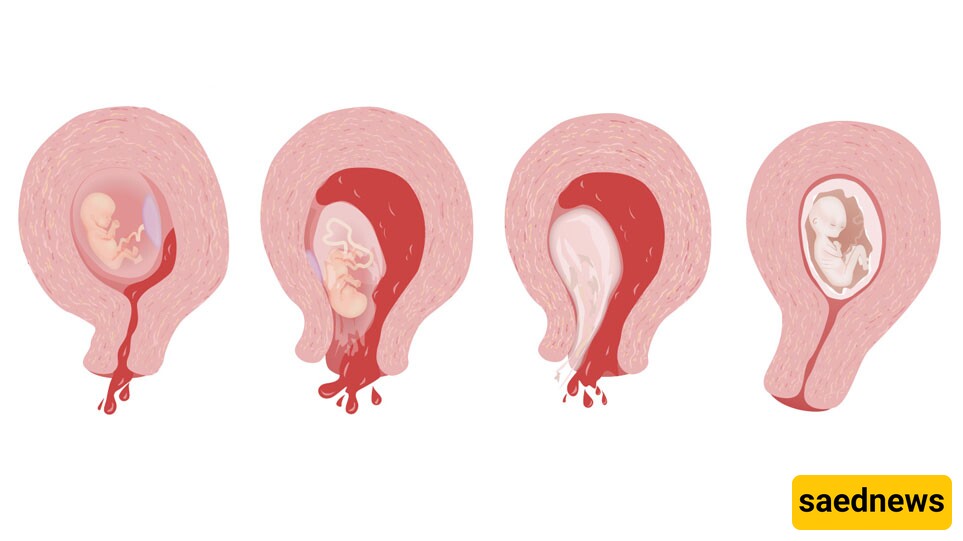
An incomplete miscarriage, which is riskier than a complete miscarriage, involves fetal death with persistent bleeding. During bleeding episodes, blood clots or fetal tissues, such as the amniotic sac or blood vessels, may pass from the body.
In some cases, bleeding may not occur, but severe abdominal pain may indicate retained fetal tissue, requiring surgical intervention. A doctor can confirm an incomplete miscarriage through ultrasound, pelvic exams, or blood tests.
IVF involves fertilizing an egg outside the body and implanting the embryo in the uterus. If the embryo fails to implant or is lost after implantation, it is referred to as implantation failure or pregnancy loss rather than miscarriage.
Signs of potential pregnancy loss in IVF include:
Vaginal bleeding
Abdominal or pelvic pain
Decreased pregnancy symptoms
There is no documented medical evidence suggesting that miscarriage occurs specifically during sleep. However, if you experience symptoms of miscarriage while sleeping, seek emergency medical attention.
Doctors recommend a healthy diet, daily exercise, and regular prenatal check-ups to maintain maternal and fetal health. Additional recommendations include:
Getting enough rest: Prioritize sleep and avoid strenuous activities.
Engaging in small leisure activities: Socialize, read, or watch TV to relax.
Avoiding stress and conflict: Protect your mental well-being.
Pregnancy is a sensitive and long journey requiring serious care. Even a small mistake or sudden incident can jeopardize maternal and fetal health, potentially leading to miscarriage.

The most critical miscarriage symptoms include:
Vaginal bleeding
Abdominal and lower back cramping
Loss of pregnancy symptoms (such as fetal movement)
To protect your pregnancy, maintain a balanced lifestyle, avoid harmful substances like tobacco and alcohol, attend prenatal checkups, and follow your doctor’s recommendations. If you notice any concerning symptoms, seek medical attention immediately.

