SAEDNEWS: Dinosphalosaurus Had 32 Separate Vertebrae and an Exceptionally Long Neck, Resembling a Chinese Dragon
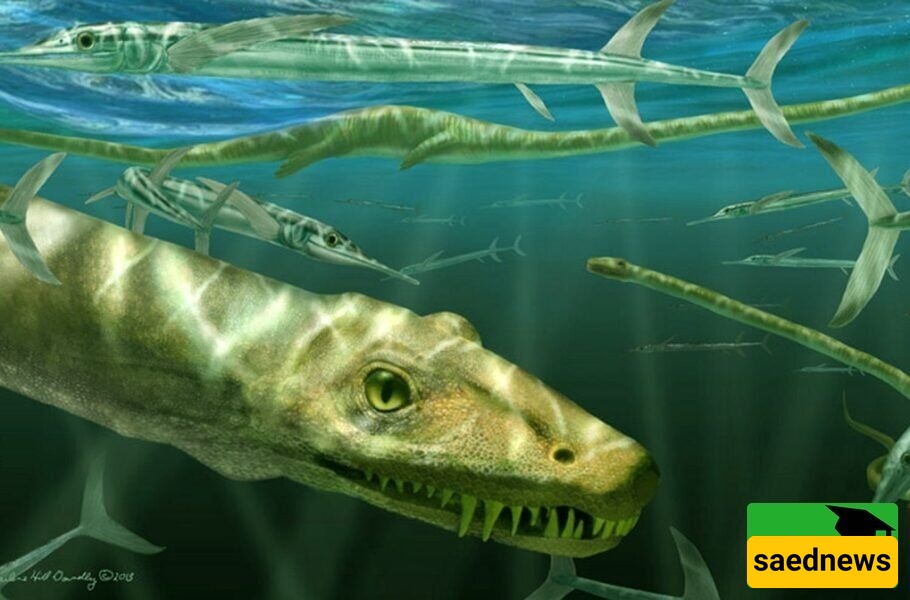

An international team of scientists from China, the United States, and Europe has uncovered new 240-million-year-old fossils of a marine reptile named Dinocephalosaurus. This research marks the first time the creature—strange, dragon-like, and long-necked—can be fully described.
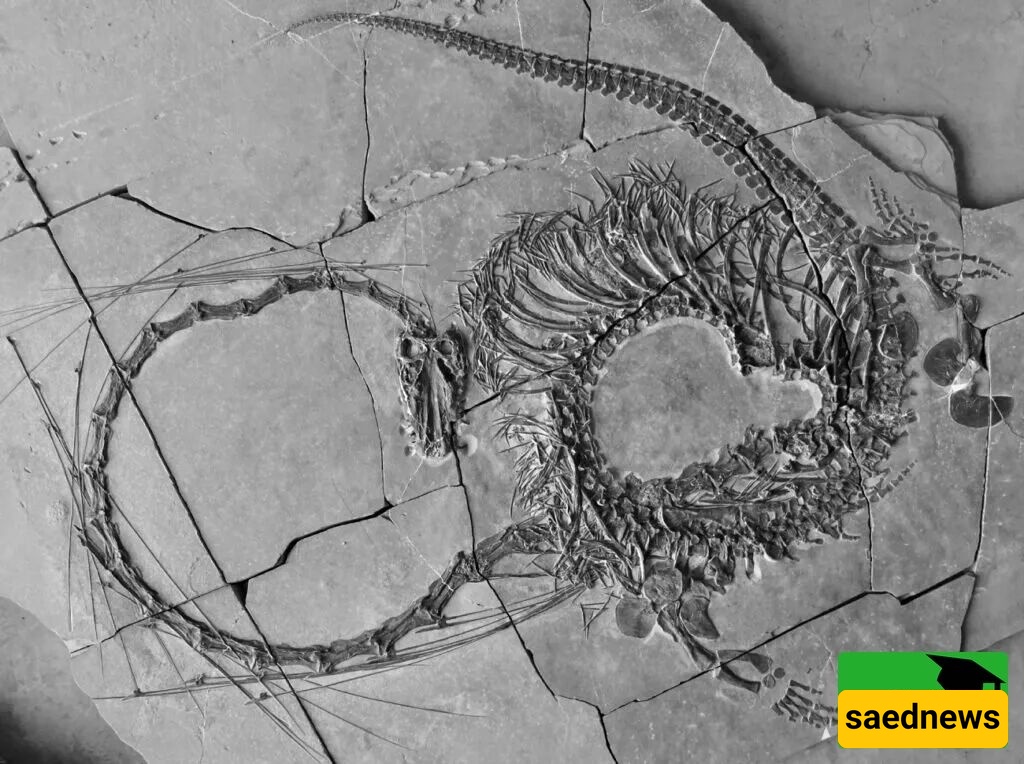
According to a study published in Earth and Environmental Science, Dinocephalosaurus had an unusually long neck reminiscent of the snake-like dragons found in Chinese mythology. In 2003, a skull and the first three cervical vertebrae of Dinocephalosaurus orientalis were discovered in Guizhou Province, China, and subsequently studied. Since then, additional specimens have been unearthed in southwest China and are now housed at the Beijing Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology. These discoveries allowed researchers, over a decade-long study, to describe nearly the entire skeleton of this marine reptile.
Paleontologists say the discovery of these additional fossils finally enabled them to visualize the long-necked animal in its entirety. Its serpentine, elongated form evokes legendary Chinese dragons. Dinocephalosaurus’s extraordinary appearance has drawn attention from experts, as even in contemporary Chinese culture, such long-necked dragons hold a unique symbolic place.
The reptile had an exceptionally long neck composed of 32 separate vertebrae, likely resembling the tanystropheid Tanystropheus, which lived in Europe and present-day China during the Middle Triassic. Both reptiles were similar in size, and several cranial features were identical.
However, Dinocephalosaurus is unique in having many more vertebrae in its neck and torso. Unlike many reptiles, it was viviparous, carrying embryos internally and giving birth to live young. It was well-adapted to ocean life, possessing fin-like limbs for swimming.
Despite superficial similarities, Dinocephalosaurus was not closely related to the later plesiosaurs—famous marine reptiles that evolved roughly 40 million years later and inspired lake monster legends.