SAEDNEWS: What is a cryptocurrency wallet address and how can you find it? In this article, learn how to identify wallet addresses in different wallets, the difference between public and private keys, types of Bitcoin addresses, and security tips. A comprehensive guide for beginners and professionals alike.
According to SAEDNEWS, in the fast-paced world of cryptocurrencies, understanding basic concepts like wallet addresses is the starting point for entering this new financial realm. Whether you are a beginner or a professional trader, knowing how to find and use wallet addresses correctly is the fundamental skill needed for security and success in this field. In this article from SaadNews, you will become familiar with the structure of addresses, access methods, and their differences in various wallets.
A cryptocurrency wallet address is like your bank account number in the world of digital currencies. This address is a unique string of letters and numbers used to receive digital currencies. Without this address, no transaction can take place. In fact, the wallet address is the destination to which digital assets are sent, ensuring transparency and security of transactions on the blockchain network.
Every digital wallet has a public key and a private key. The public key is your wallet address, which you can share with others. In contrast, the private key is like your bank password and should not be shared with anyone. This key grants full access to your assets, and losing or revealing it could lead to permanent loss of your digital assets.
Creating a digital wallet depends on its type. Software wallets can be downloaded from applications like Trust Wallet or MetaMask. Hardware wallets like Ledger need to be physically purchased. There are also paper wallets that print wallet keys. In all these cases, once the wallet is installed or obtained, a unique address for each cryptocurrency is automatically generated.
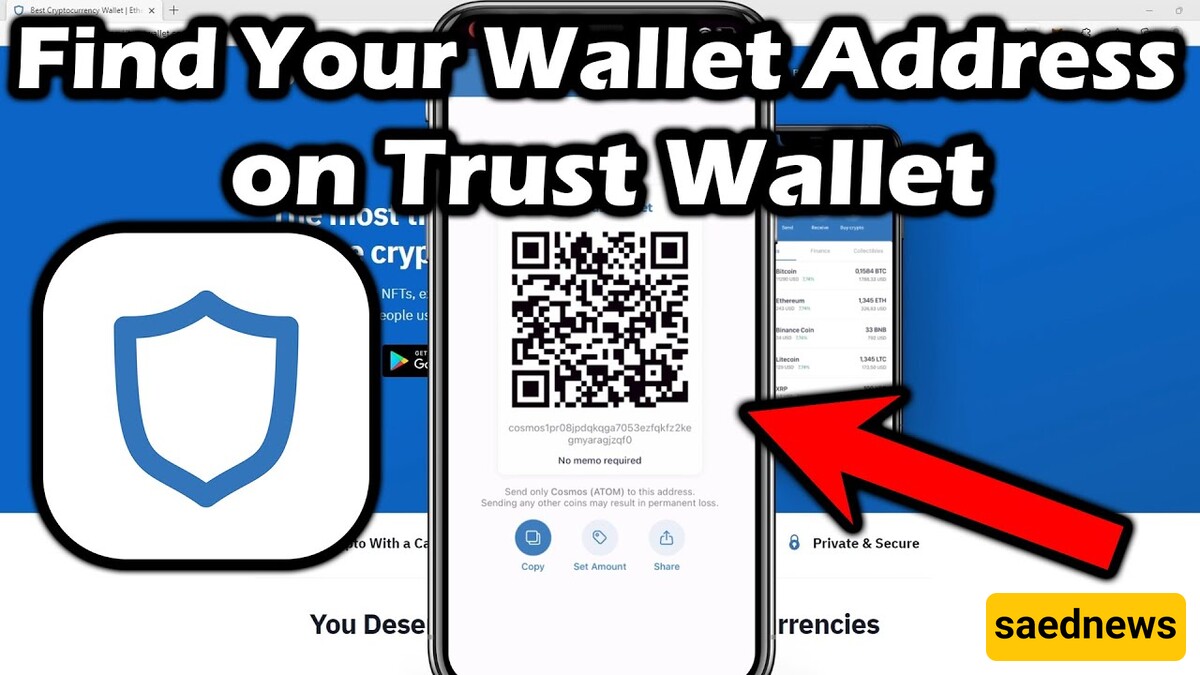
Finding your wallet address is easy in most apps. Simply enter your wallet, select the desired currency, and tap the "Receive" option. For example, in Trust Wallet or Atomic Wallet, you can view your public address as a QR code or a text that can be copied with just a few clicks. This process is similar in wallets like Coinomi, MetaMask, and SafePal.
Examples of Bitcoin Wallet Addresses Bitcoin addresses come in different formats, beginning with characters like 1, 3, or bc1. Each of these formats, such as Legacy, Segwit, or Taproot, has its specific use. Recognizing these differences helps users understand the type of address they are dealing with and which features, like lower fees or higher security, they provide.
Tether addresses differ depending on the network you choose. For instance, Tether’s address on the Tron network starts with "T" or "TX" and follows the TRC-20 standard, while on Ethereum, it starts with "0x" and follows the ERC-20 standard. Choosing the correct network and address for sending or receiving Tether is crucial, as errors in this regard can lead to asset loss.

Since the cryptocurrency world is decentralized and lacks a governing body, the complete responsibility for protecting assets lies with the user. Choosing a reputable wallet, backing up private keys, and being careful when sharing addresses are key points in managing digital assets. A small mistake can be irreparable.
A wallet address is your gateway to the decentralized and transparent world of cryptocurrencies. By understanding different types of addresses, paying attention to network differences, and using public and private keys correctly, you can manage your digital assets with greater confidence. Remember, security and accuracy in this process are the keys to lasting success in the digital currency space.

