SAEDNEWS: Once a vast salt lake in Iran, Lake Urmia has suffered severe depletion due to environmental changes and human impact. Efforts to restore this unique ecosystem are ongoing, though the challenges remain significant.
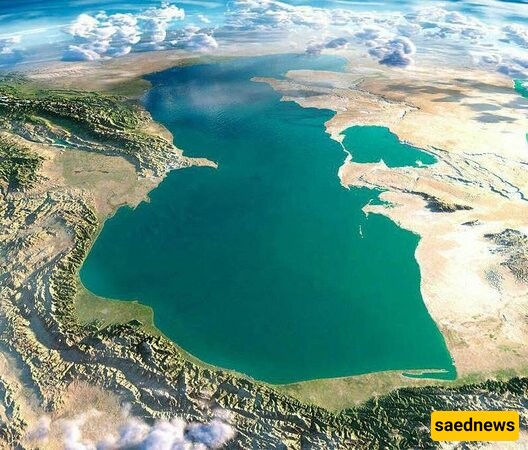
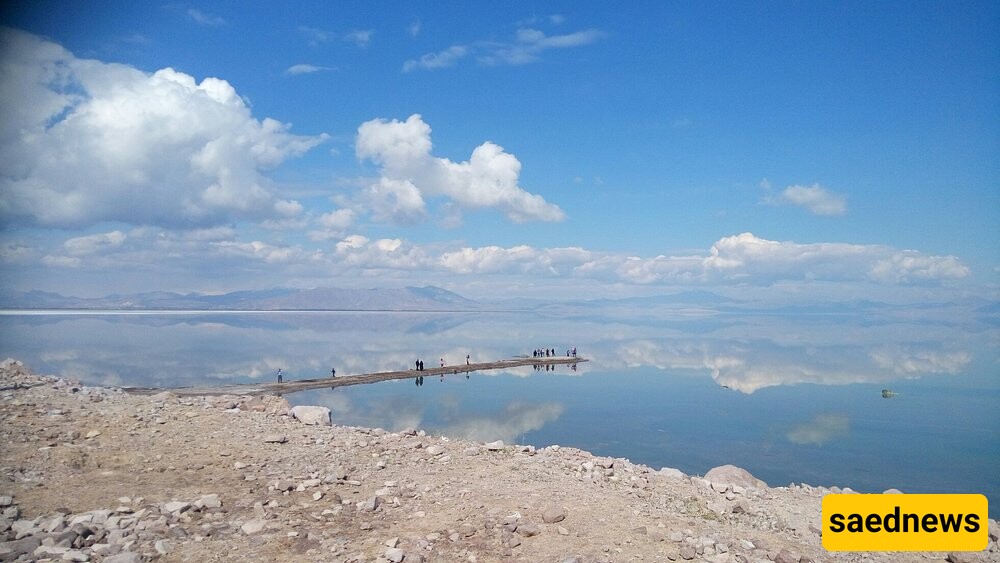
According to SAEDNEWS, nestled between the Iranian provinces of East and West Azerbaijan, Lake Urmia was once the largest saltwater lake in the Middle East and the sixth largest in the world. In recent years, however, the lake has shrunk dramatically due to factors like climate shifts, water overuse, and dam construction. Today, the focus on reviving Lake Urmia is stronger than ever, as its value for biodiversity, climate, and tourism has become increasingly clear.
A Symbolic Natural Wonder
As one of Iran’s most iconic natural sites, Lake Urmia has long held cultural and ecological significance. It has served as a habitat for a variety of species, including migratory birds such as flamingos and pelicans. The lake also drew tourists for its reputed healing salts and scenic views, especially during sunset, when the lake’s red hues would reflect in a captivating display.
Role in Regional Climate Stabilization
The lake has been crucial for local climate stability, helping to moderate temperatures and reduce dust storms. It even played a role in maintaining rainfall patterns that benefit nearby agricultural areas—a valuable buffer against extreme weather that has been sorely missed as the lake recedes.
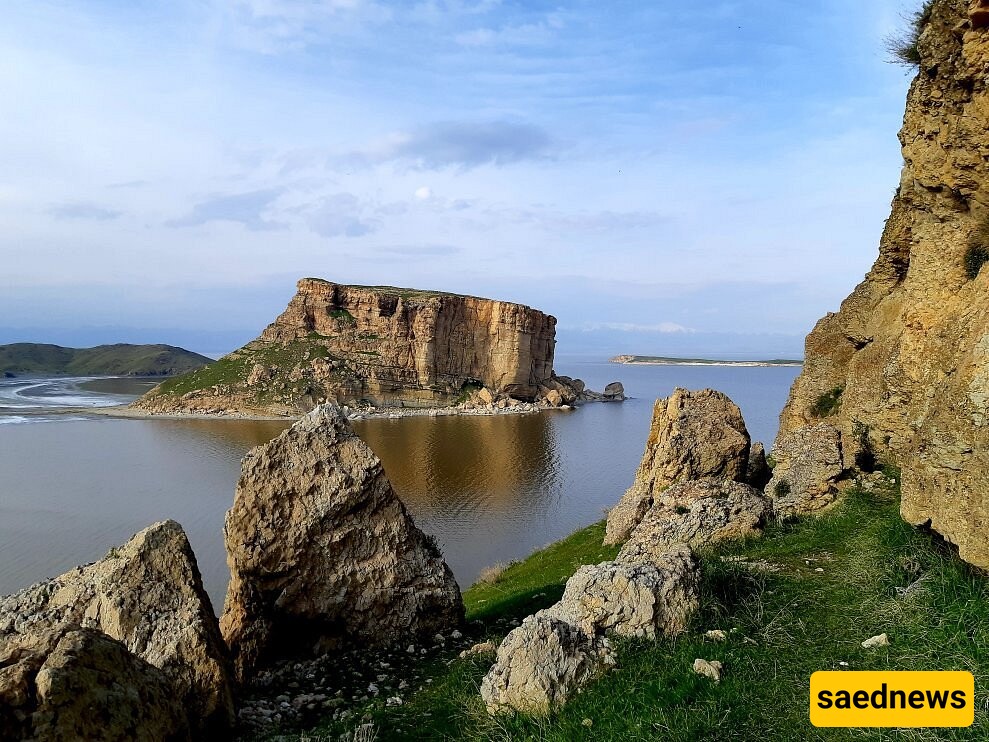

Impact of Climate Change
Iran has faced increasingly severe droughts, temperature hikes, and erratic rainfall, all of which have intensified Lake Urmia's shrinkage. As a result, the lake is losing water at an alarming rate, adding urgency to the region’s conservation efforts.
Human Intervention: Dams and Water Redirection
Human activities have significantly contributed to the lake’s decline. Over 50 dams were built on rivers feeding Lake Urmia, while water from these sources was diverted to support agriculture. With far less water entering the lake, its levels fell, and the salt concentration increased, creating a harsh environment for aquatic life and the surrounding ecosystem.
Rising Salinity Levels
The decrease in freshwater inflow has led to higher salt levels, which harm local species and dry out the lakebed. The exposed salt flats, in turn, contribute to frequent dust storms that affect nearby towns and farms, spreading salt across the soil and harming agricultural productivity.
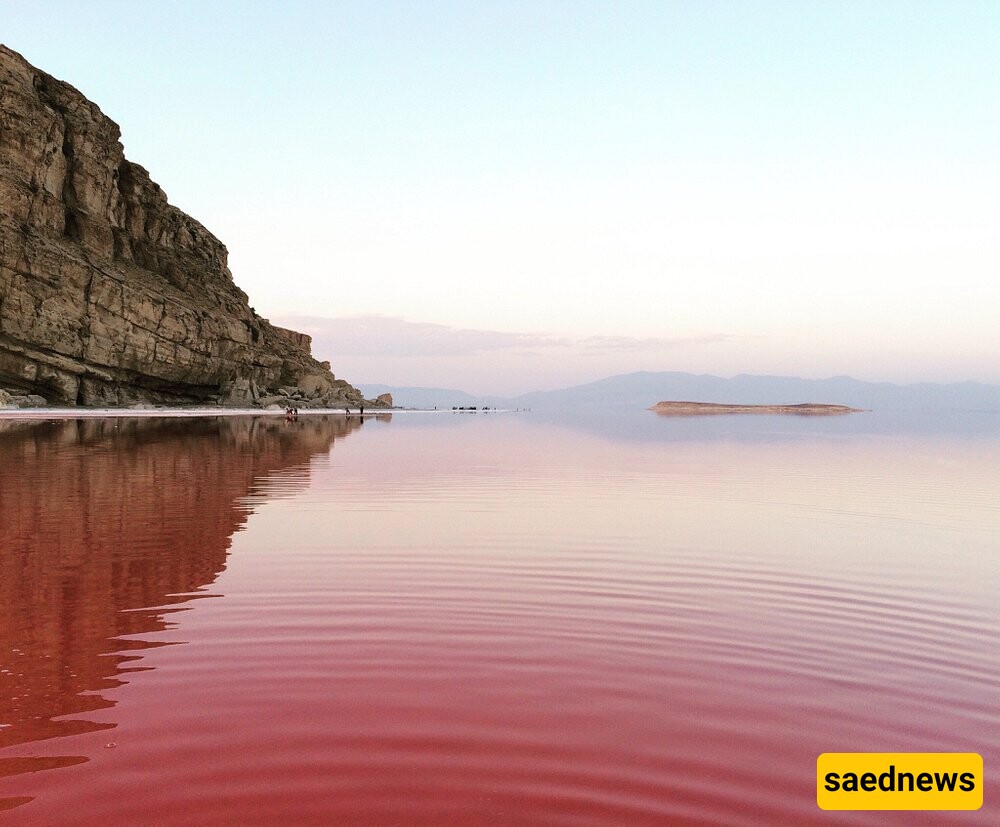

Economic Loss for Local Residents
The shrinking lake has severely impacted the local economy. Tourism, once a major source of income due to the lake’s natural beauty, has dwindled, while fishing opportunities have also declined as the lake's ecosystem suffered. These changes have disrupted the lives of people who once depended on the lake’s resources.
Health and Environmental Risks
The exposed salt beds have become sources of salt-infused dust storms, posing health risks for communities near the lake. Respiratory issues and eye irritations are now common, and the salt carried by these storms damages farmlands, reducing crop yields and soil fertility.
Government and International Projects
In 2013, the Iranian government, in collaboration with international partners, launched the Lake Urmia Restoration Program (LURP). This initiative aims to reduce water use, improve water resource management, and restore some of the lake’s lost volume by improving water flow and conservation efforts.
Reducing Water Use in Agriculture
One of the main objectives has been to limit water use in agriculture, historically the biggest contributor to the lake’s water depletion. By introducing efficient irrigation systems like drip irrigation and promoting water-saving practices, authorities are encouraging farmers to adopt more sustainable methods. Additionally, they are supporting a transition to less water-intensive crops.
Regulated Water Releases from Dams
Controlled water releases from upstream dams are another strategy to help Lake Urmia regain its volume. By carefully managing water flow, authorities hope to strike a balance between the lake’s needs and the requirements of nearby communities who also depend on this vital water source.
Reforestation to Combat Dust and Erosion
To help reduce soil erosion and limit dust storms, reforestation efforts around the lake have been implemented. Planting native trees and vegetation helps stabilize the soil and improve the microclimate, creating better conditions for the lake’s potential recovery.

High Water Demand
Despite ongoing restoration efforts, Iran’s need for water, particularly for agriculture, remains a major obstacle. Balancing human needs with environmental conservation is complex in a water-scarce region, and sustainable water management is critical to Lake Urmia’s future.
Climate Change Impacts
Climate change continues to present challenges, bringing erratic weather that complicates efforts to restore the lake. Prolonged droughts and unpredictable rainfall patterns make it difficult to maintain the consistent water levels needed for the lake’s revival.
Public Awareness and Long-Term Engagement
For restoration to succeed, long-term commitment is essential. Public awareness campaigns have helped educate locals about the importance of water conservation, but widespread engagement is still needed to ensure sustainable practices are maintained and respected.
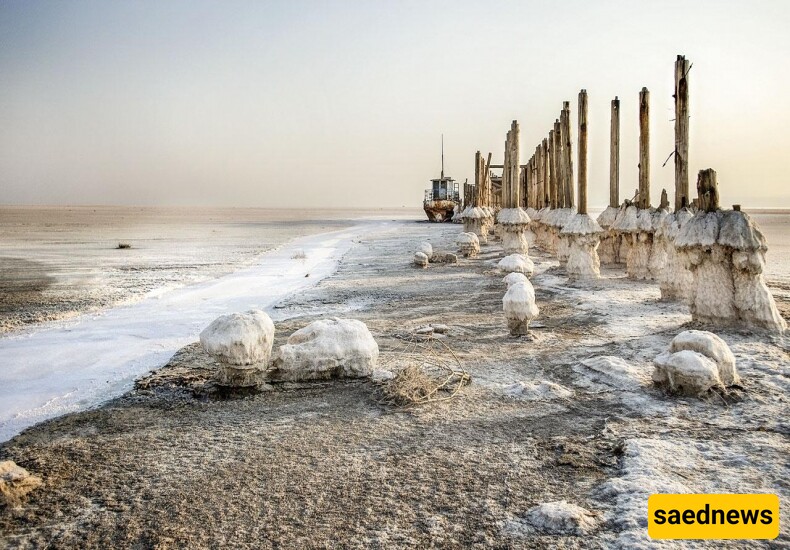

Lake Urmia remains a symbol of Iran’s environmental heritage and the urgent need for sustainable water management. With continued government action, international support, and the involvement of local communities, there is hope for the lake’s revival. However, the path forward is challenging, requiring resilience and adaptability to protect this unique ecosystem. Lake Urmia’s story serves as a call to preserve our planet’s natural wonders and secure them for future generations.

