The benefits of exercise are being discovered more and more every day, and it also has a positive impact on the internal organs of the body, contributing to their health. The gut is one of these organs.
Exercise is extremely beneficial for you. Regular exercise helps maintain a healthy weight, improve sleep, boost mood, and increase energy. Studies show that exercise is one of the best activities you can do throughout the day to reap all its benefits. But what exercise can you do to address gut problems or strengthen the gut effectively? In this section of Saadnews, we will discuss bowel obstruction, its causes, and how to treat it with exercise. Stay with us.
The intestines constantly perform wave-like muscle contractions known as peristalsis. Peristalsis moves food, gas, and stool forward to be eliminated from the body. When a section of the intestine slows down or stops moving, it can cause the stool to accumulate, creating a blockage. This condition is known as intestinal obstruction, where the movement of the bowels ceases, resulting in stool accumulation.
Bowel obstruction does not occur in healthy individuals with no pre-existing conditions. However, certain conditions increase the risk of developing this issue, including:
Surgery, especially digestive system surgeries
Electrolyte imbalance
Crohn's disease
Colon cancer
Abdominal injury
Medications (opioids, anticholinergics, and sometimes calcium channel blockers)
Metabolic disorders
Typically, the muscles in the intestines contract and relax to create peristalsis, which helps move food through the intestines. When an obstruction occurs, the peristaltic system stops, preventing the passage of food, gas, and fluids through the digestive tract.
If individuals continue to eat solid foods, food particles accumulate, inevitably causing a partial or complete intestinal obstruction. This condition usually occurs after abdominal or pelvic surgery. According to some estimates, bowel obstruction is the second most common cause of readmission to the hospital in the first month after surgery. This condition can occur due to the following:
Slow return of normal peristalsis after surgery
Medications prescribed after surgery affecting bowel movement
Scar tissue from surgery causing blockage
Certain drugs affecting the muscles and nerves of the digestive system, such as:
Opioid pain relievers
Anticholinergics used to treat various conditions, including bladder problems, COPD, and Parkinson's disease
Calcium channel blockers used for heart diseases
Other causes of bowel obstruction include:
Infections and muscle or nerve disorders, such as Parkinson's disease
In children, "intussusception" often causes ileus. This is when a part of the intestine slides into itself, like a telescope closing.
Now, let's look at some effective and beneficial exercises to strengthen the gut:
Yoga is one of the best methods to calm your mind. People who struggle with stress often suffer from digestive problems and may experience symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Yoga can help mentally calm them and alleviate stress-induced conditions like IBS.

One of the exercises recommended for strengthening the gut is light jogging, which helps your stomach and intestines function better. If you can't jog, try skipping rope, and if you don't have a jump rope, you can use a treadmill. The key is to get your body sweating.
Walking is an effective method to help calm your mind and doesn't require much effort. It also doesn't need any special equipment, improves your digestion, and is particularly effective for those with irritable bowel syndrome.

Swimming is one of the best exercises you can do to improve joint, gut, and stomach health. It boosts your mood and increases the good bacteria in your stomach and intestines.
Cycling outdoors or using a stationary bike in the gym is one of the best exercises for digestive health. Research shows that cycling at moderate or even low intensity for up to three hours a week increases the beneficial bacteria in the gut.
The elliptical machine, like walking, jumping rope, and cycling, is one of the best options for improving stomach and gut health. Its biggest advantage is that you don't need to exert yourself too much, and it engages your lower body, strengthening your abdominal area and internal organs.
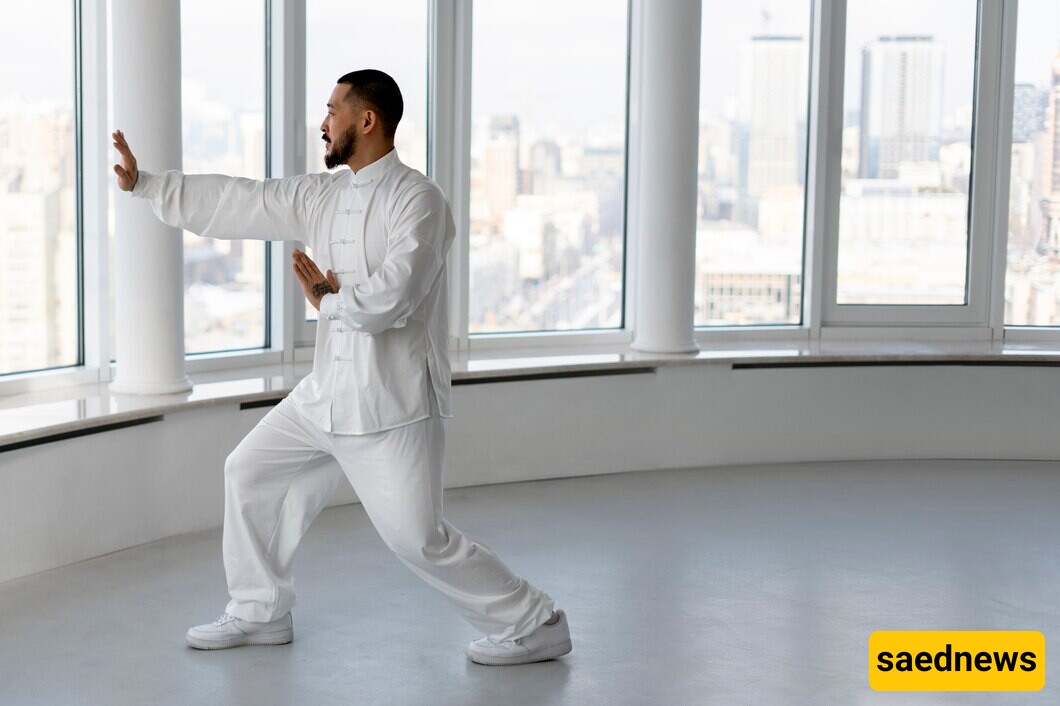
Tai Chi is a gentle exercise, especially popular in China, that improves digestive problems. Its slow and focused movements improve spinal health, which in turn strengthens the stomach and intestines, alleviating constipation and other digestive issues.


