SAEDNEWS: You’ve probably heard the saying, ‘you are what you eat,’ and research is showing this to be truer than ever.

According to SAEDNEWS: when we think about ways to improve our mental health, we frequently consider therapy, exercise, mindfulness, or medication. Diet, on the other hand, is an important but sometimes disregarded aspect. What you eat has a big impact on your brain health, emotions, and general mental well-being.
Your brain, like the rest of your body, requires adequate nourishment to function correctly. In this blog, we'll look at how your diet may impact your mental health, the relationship between your stomach and brain, and which foods might help you feel better—and which should be avoided.
Research has increasingly proven a direct link between what we eat and how we feel psychologically. A poor diet can cause mood changes, exhaustion, and even raise the risk of mental health disorders including anxiety and depression. On the other hand, a well-balanced, nutrient-dense diet can help calm moods, boost energy levels, and promote long-term brain health.
The developing subject of nutritional psychiatry investigates how diet affects brain chemistry and mental health. Experts believe that the appropriate foods may nourish the brain, increasing cognitive performance, attention, and emotional resilience. Dr. Felice Jacka, A major researcher in this field performed tests that found that those who followed a Mediterranean-style diet rich in whole foods had far less depressive symptoms than those who ate processed, sugary meals.
What's the takeaway? Food may be both physical and mental medicine.
The gut-brain axis, which connects your digestive system to your brain, has been one of the most interesting discoveries in recent years. The gut microbiome is the aggregate name for billions of microorganisms that live in your gut. These bacteria create neurotransmitters such as serotonin, which regulates mood, sleep, and behavior. In reality, your stomach, rather than your brain, produces roughly 90% of serotonin. As a result, poor gut health can have a direct influence on your mental state.
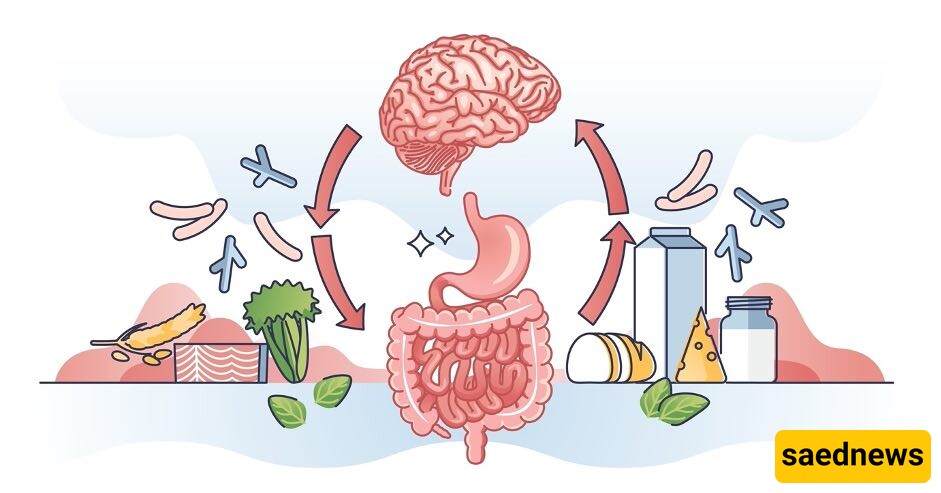
Food's Impact on Gut-Brain Axis
1. Processed Foods and Sugar - Diets heavy in processed foods, refined carbohydrates, and unhealthy fats can trigger gut inflammation, resulting in altered brain signaling and mood swings.
2. Probiotic and prebiotic foods - Foods such as yogurt, kefir, kimchi, and fiber-rich vegetables promote good gut flora, which enhances neurotransmitter synthesis and brain function.
3. Omega 3 Fatty Acids - Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids include fatty fish, chia seeds, and walnuts. These necessary fats lower inflammation and support healthy brain function, which can aid with anxiety and sadness.
In summary, nourishing your stomach nourishes your intellect.
Omega-3 fatty acids are needed for brain function. They lower inflammation, increase communication between brain cells, and promote general cognitive health. What to eat ?
- Fatty fish, including salmon, sardines, and mackerel.
- Flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts.
Benefit: According to research, omega-3 fatty acids can help alleviate symptoms of sadness and anxiety.
B vitamins, notably B6, B12, and folate, play important roles in energy generation and neurotransmitter modulation. bad levels of B vitamins have been related to weariness, irritation, and bad mood. What to eat ?
- Leafy greens, like spinach and kale.
- Eggs and dairy products.
- Legumes, entire grains
Benefit: B vitamins assist the brain create serotonin and dopamine, which are neurotransmitters that govern mood and happiness.
Magnesium is a mineral that helps to relax the nervous system and improves sleep quality, both of which are important for mental health. Foods To Eat:
- Dark chocolate (Yes, chocolate!)
- Nuts, including almonds and cashews
- Whole grains and avocados.
Benefit: Magnesium can help to alleviate anxiety and increase relaxation.
Proteins include amino acids, which are the building blocks for neurotransmitters such as serotonin and dopamine. Foods To Eat:
- Lean meats (chicken and turkey); Eggs and tofu; Nuts and legumes
Benefit: Eating enough protein maintains your brain's chemistry regulated and your mood steady.
Antioxidants combat oxidative stress, which can harm brain cells and lead to mental health issues. Foods To Eat:
- Berries (blueberries, strawberries) - Vegetables (carrots, broccoli, sweet potatoes).
- Green Tea
Benefit: Antioxidants protect brain cells and prevent inflammation, resulting in increased mental clarity and attention.
While including nutrient-dense foods in your diet is vital, you should also avoid items that have a detrimental influence on your brain and mood.
Refined sugar - Excess sugar elevates blood sugar levels, resulting in energy dumps and emotional fluctuations. It may also affect the gut microbiota. Avoid sodas, candies, pastries, and sugary cereals.
Processed meals Junk and fast food include harmful fats, preservatives, and chemicals that can cause inflammation and poor mental health. Avoid chips, fried meals, quick noodles, and processed meats.
Caffeine (in excess) - Caffeine can increase concentration in modest quantities, but too much can cause anxiety, jitters, and interrupted sleep.

1. Begin small and gradually adjust your diet. Replace sugary snacks with fruits, eat a serving of fish per week, or incorporate leafy greens into your meals.
2. Prioritize entire, unprocessed foods, such as vegetables, fruits, nuts, and lean meats.
3. Eat a "Rainbow."- Different colored meals have different nutrients. Aim to use a range of colors on your dish.
4. Stay hydrated - Dehydration can impair energy levels and cognitive function.Aim for at least 8 glasses of water each day.
5. Plan and Prepare Meals. - Meal planning allows you to make healthier eating choices throughout a hectic week.
The relationship between food and mental health is apparent. What you consume fuels not just your body, but also your intellect. A diet high in omega-3 fatty acids, B vitamins, magnesium, and antioxidants can boost your mood, reduce anxiety, and improve cognitive performance.
Simultaneously, limiting processed meals, sweets, can significantly improve your emotional well-being. When you're feeling down, apprehensive, or muddled, consider staring at your plate. Small dietary adjustments may have a significant impact on how you think, feel, and manage life. After all, mental wellness is more than just the head; it begins with how you fuel your body. So, are you prepared to eat your way to improved mental health? Begin now, one meal at a time.

