SAEDNEWS: Biometric technology is revolutionizing security, offering personalized and efficient ways to protect data, devices, and facilities. By replacing traditional passwords, biometrics is setting a new standard for safety and convenience.

According to SAEDNEWS, biometric technology, which uses unique physical and behavioral traits to verify identity, is rapidly reshaping security protocols. With cyber threats increasing and data breaches becoming more sophisticated, the limitations of traditional passwords and keycards are clear. Biometrics promises greater accuracy, efficiency, and personalization, positioning it as the cornerstone of next-generation security.

Biometric authentication identifies individuals based on unique characteristics, such as fingerprints, facial features, voice patterns, or even gait. These traits are analyzed using advanced algorithms, creating a secure, non-transferable digital signature. This personalized approach minimizes the risk of identity theft and unauthorized access.
Fingerprint Scanning
One of the most common biometric methods, fingerprint scanning is widely used in smartphones, access control systems, and banking apps. Its affordability and ease of integration make it a popular choice for everyday applications.
Facial Recognition
Facial recognition maps facial features using artificial intelligence. Airports and secure facilities frequently adopt this technology for seamless identity verification. While highly accurate, concerns about privacy and misuse have sparked ongoing debates.
Iris and Retina Scanning
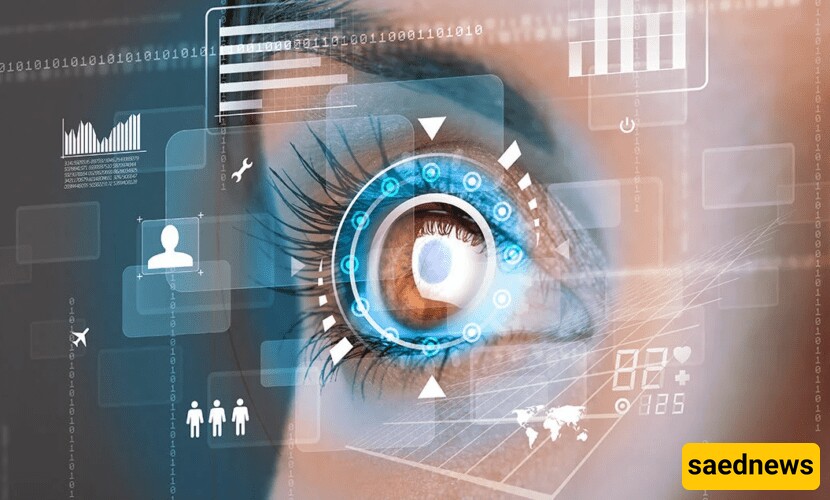

Iris and retina scanning offer an even more precise biometric solution, leveraging the unique patterns in the eye. Though highly reliable, this method requires specialized hardware, limiting its widespread adoption.
Voice Recognition
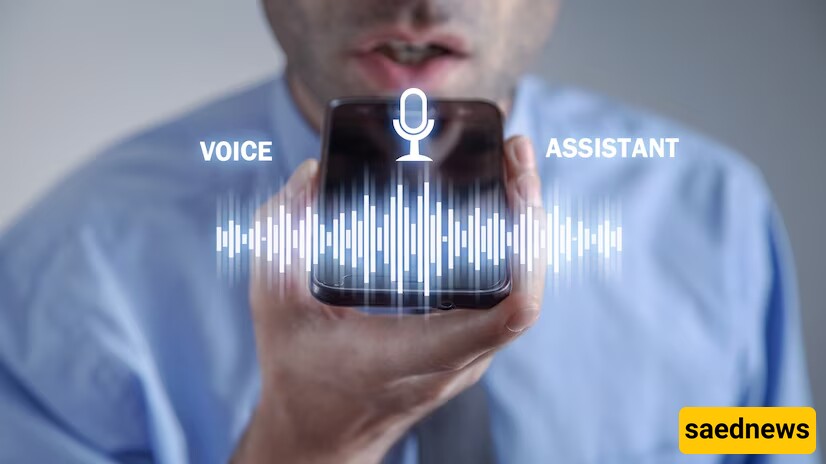

Voice recognition technology analyzes vocal patterns for identification. It is often used in customer service systems and smart devices, offering a hands-free security option.
Behavioral Biometrics

Unlike physical biometrics, behavioral methods track unique habits, such as typing speed, mouse movements, or walking style. This emerging field enhances security by detecting anomalies in user behavior.
Biometric technology is transforming various industries by enhancing security and convenience. In the banking and financial services sector, biometrics is replacing traditional PINs and passwords with fingerprint or facial scans, reducing fraud and improving user experience. Similarly, in healthcare, biometric systems ensure patient confidentiality and provide secure access to medical records, while also controlling staff entry to sensitive areas within hospitals and clinics.
In travel and transportation, airports worldwide are implementing biometric solutions for faster check-ins and boarding, replacing traditional ID checks with facial recognition to enhance both security and efficiency. Corporate and government facilities also rely on biometric systems, such as fingerprint scanners, facial recognition, and iris scans, to restrict access to authorized personnel and safeguard sensitive areas.
Meanwhile, consumer technology is increasingly integrating biometrics into everyday devices like smartphones and gaming consoles. This development not only simplifies security measures but also offers a more personalized user experience, marking a significant shift in how technology interacts with users.
Enhanced Security
Biometric systems are far more secure than traditional methods like passwords or keycards, which can be lost, stolen, or hacked. Physical traits are unique and difficult to replicate, making biometrics a robust defense against unauthorized access.
Convenience and Speed
Biometric authentication eliminates the need for remembering passwords or carrying physical tokens. It enables quick, seamless access to devices, accounts, and facilities, improving user satisfaction.
Fraud Prevention
By relying on unique identifiers, biometrics significantly reduces identity theft and financial fraud. Advanced algorithms detect even minor discrepancies, thwarting potential breaches.
Despite its benefits, biometric technology faces hurdles that need to be addressed.
Collecting and storing biometric data raises concerns about misuse, surveillance, and unauthorized access. Organizations must prioritize data encryption and adhere to privacy regulations to build user trust.
Implementing biometric systems requires significant investment in hardware, software, and infrastructure. While prices are decreasing with advancements, initial costs remain a barrier for smaller organizations.
Unlike passwords, biometric data cannot be reset if compromised. A breach of this sensitive information can have long-term consequences, emphasizing the need for robust security measures.
Biometric systems are not foolproof. Factors like poor lighting, device quality, or changes in physical appearance can affect accuracy, leading to potential errors in identification.
Biometric technology continues to evolve, driven by advancements in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and sensor development. Emerging trends include:
Combining multiple biometric methods, such as fingerprint and facial recognition, enhances accuracy and reliability. This approach is gaining traction in high-security sectors.
The rise of biometric payment systems, where users verify transactions using fingerprints or facial scans, is transforming retail and e-commerce.
Wearables equipped with biometric sensors, such as smartwatches, are expected to expand the scope of biometric applications.
To address privacy concerns, researchers are exploring decentralized systems where biometric data is stored on individual devices rather than centralized databases.
Biometrics is reshaping security, providing a sophisticated, personalized alternative to traditional methods. While challenges like privacy and cost must be addressed, the potential benefits of enhanced security and user convenience make biometrics an essential part of the digital age. As technology advances, biometrics will likely become the global standard for secure authentication, bridging the gap between safety and simplicity.

